It can be frustrating to be interrupted when you are concentrating on a task, but a good employee knows they must respond to questions and interruptions politely. Some students may become agitated when asked to transition from their activity, or may not know how to interpret the body language of the person speaking to them. They may then choose to ignore the interruption, or respond in frustration. It is important to develop the skills to respond calmly and with pleasant body language, to shift attention from one task to another, to listen to what the other person is saying or asking, and to respond or take action as necessary. Rather than ignoring interruptions by others, students should practice using self-calming strategies and conversational scripts to encourage an appropriate response to interruptions.
Questions & Interruptions
 Guiding Questions
Guiding Questions
- Are the student’s verbal responses limited by difficulty processing verbal information or questions?
- Is the student attending to non-verbal cues (body orientation, eye contact, voice volume, other environmental cues) to determine if someone is talking to him?
- Does the student have verbal coping strategies to assure that he understands what is said?
- Is the student agitated or confused when he has to shift his focus from anactivity to someone speaking?
- What coping strategies does the student need to remain calm or to ‘act responsively’ without signs of irritation?
Visual Supports

Communication systems and scripts
provide the student with a means to initiate communication. Use these
cards to practice different scenarios with your students.
|
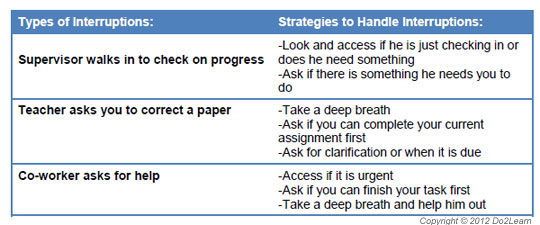
Graphic organizers can
provide a student with a way to represent and organize concepts,
thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and potential outcomes.
|

Social narratives
are a set of tools that visually represent social situations and
appropriate social behaviors. The social narrative connects the
important details of a setting or social situation to support the
student in understanding the social context and in developing a new
social skill.
|
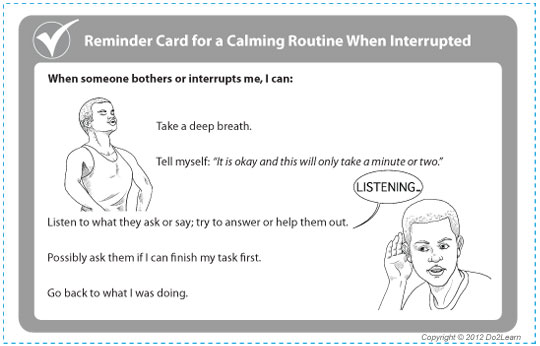
Visual Cues are learning materials that students can keep with them to help guide them through real life situations.
|
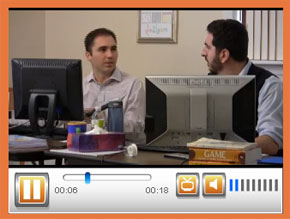
Video modeling involves the use of video recording as
a teaching tool. It involves a student watching a video of the
appropriate performance of a task (expected behavior) prior to
practicing or potentially using the skill in natural settings.
|
|
Does the design of space and furniture help the student focus on the tasks and behaviors expected in the setting? If the student is at an office job site, the furniture or his desk could be moved or arranged so he is not facing the entrance or is not visible from the door to discourage interruptions. Some students might need to be in a separate part of the work site out of the main stream of customers or co-workers to minimize potential interruptions or confusing questions. |










